Humidity plays a significant role in mold formation, making it essential to manage moisture levels in our homes and other indoor spaces. Excessive humidity provides the ideal conditions for mold growth, posing potential health risks and structural damage. In this blog post, we will explore the role of humidity in mold formation, its effects on our living environment, and effective strategies for managing moisture levels to prevent mold growth.

Understanding Humidity and Mold
Humidity refers to the amount of moisture present in the air. It is measured as a percentage and can vary depending on factors such as weather, ventilation, and indoor activities. Mold, on the other hand, is a type of fungus that thrives in damp and humid environments. When humidity levels exceed a certain threshold, typically above 60%, it creates an environment conducive to mold growth.
How Humidity Contributes to Mold Formation
High humidity creates the ideal conditions for mold growth by providing the moisture necessary for mold spores to germinate and thrive. Here’s how humidity contributes to mold formation:
- Moisture Accumulation: Excessive humidity causes moisture to accumulate on various surfaces, such as walls, ceilings, floors, and furniture. This moisture serves as a nutrient source for mold, allowing it to grow and spread.
- Condensation: When warm, humid air comes into contact with cooler surfaces, condensation occurs. Condensation provides an additional source of moisture, particularly on windows, pipes, and other areas prone to temperature differences. This moisture creates a favorable environment for mold growth.
- Lack of Ventilation: Insufficient ventilation traps excess moisture indoors, promoting high humidity levels. Without proper airflow, moisture lingers and creates a breeding ground for mold.
Effects of High Humidity and Mold Growth
High humidity levels and mold growth can have various negative effects on our living environment:
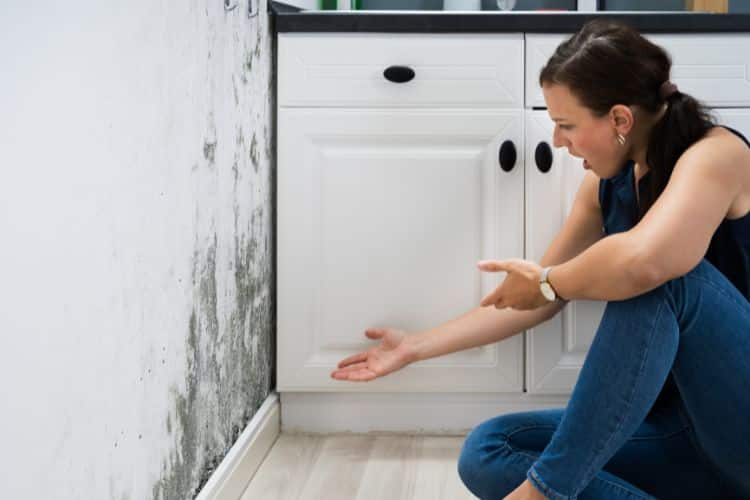
- Health Risks: Mold releases spores into the air, which can be inhaled and cause allergic reactions, respiratory issues, and other health problems. Prolonged exposure to mold spores can worsen existing conditions like asthma and allergies, and even lead to the development of new sensitivities.
- Structural Damage: Mold can cause significant damage to buildings and structures. It feeds on organic materials such as wood, drywall, and fabric, weakening their integrity over time. Structural damage can result in costly repairs and compromise the safety of the building.
- Unpleasant Odors: Mold growth often produces a musty odor that can permeate the entire space. These unpleasant odors can be persistent and difficult to eliminate, affecting the overall comfort and enjoyment of the living environment.
- Aesthetics and Property Value: Mold growth is unsightly and can tarnish the appearance of walls, ceilings, and other surfaces. Additionally, the presence of mold can significantly impact the value of a property, making it challenging to sell or rent if not remediated.
Managing Moisture Levels and Controlling Humidity
To prevent mold growth and maintain a healthy living environment, it is crucial to manage moisture levels and control humidity. Here are effective strategies for managing humidity:
- Use Dehumidifiers: Dehumidifiers are devices that remove excess moisture from the air. They are particularly useful in areas with high humidity or poor ventilation, such as basements, bathrooms, and laundry rooms. Set the dehumidifier to maintain an optimal humidity level, usually between 30% and 50%.
- Increase Ventilation: Proper ventilation helps reduce humidity levels by allowing fresh air to circulate and carry away excess moisture. Open windows and doors whenever possible, especially during mild and dry weather conditions. Additionally, use exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens to remove moisture at the source.
- Repair Leaks and Address Water Intrusions: Promptly repair any leaks in pipes, roofs, or windows to prevent water from entering your home. Regularly inspect your property for signs of water intrusion, such as damp spots, water stains, or musty odors. Addressing water issues promptly helps prevent moisture buildup and mold growth.
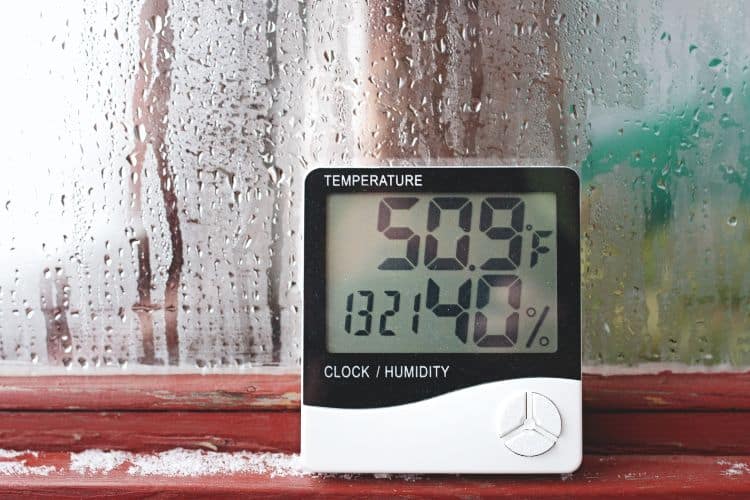
- Monitor Indoor Humidity: Use a hygrometer to monitor indoor humidity levels. Ideally, maintain humidity below 60% to discourage mold growth. If humidity levels consistently exceed this threshold, implement dehumidification measures and consider additional ventilation options.
- Proper Insulation and Vapor Barriers: Ensure your home is properly insulated to prevent condensation and moisture accumulation. Insulate cold surfaces, such as windows and pipes, to prevent temperature differentials that lead to condensation. Install vapor barriers in areas prone to moisture, such as crawl spaces, to prevent moisture migration.
- Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Regularly clean and maintain your living environment to prevent the buildup of moisture and potential mold growth. Wipe down surfaces, address spills promptly, and ensure proper ventilation during activities that generate moisture, such as cooking and showering.
Effective Moisture Control in Specific Areas
Certain areas in your home require extra attention when it comes to moisture control. Here are some specific tips for managing moisture in these areas:
Bathroom: Use exhaust fans or open windows during and after showering to reduce moisture buildup. Wipe down wet surfaces, including shower walls and fixtures, to prevent moisture accumulation. Regularly clean bathroom tiles and grout to prevent mold growth.
Kitchen: Proper ventilation is crucial in the kitchen, where cooking activities generate steam and moisture. Use range hoods or exhaust fans while cooking to remove excess moisture. Clean spills and address any plumbing issues promptly to avoid water damage and mold growth.
Basement and Crawl Spaces: These areas are prone to high humidity and moisture problems. Ensure proper insulation and vapor barriers to prevent moisture migration. Consider using dehumidifiers or installing a sump pump system to control moisture levels. Regularly inspect for any water leaks or cracks in the foundation.
Attic: Adequate attic ventilation is essential for preventing moisture buildup, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage. Ensure proper insulation and ventilation, including soffit vents, ridge vents, or attic fans, to promote air circulation and moisture control.
Conclusion
Managing moisture levels and controlling humidity is crucial for preventing mold growth and maintaining a healthy living environment. Excessive humidity creates conditions favorable for mold formation, leading to potential health risks and structural damage. By implementing effective strategies such as using dehumidifiers, increasing ventilation, repairing leaks, monitoring indoor humidity, and practicing regular cleaning and maintenance, you can reduce